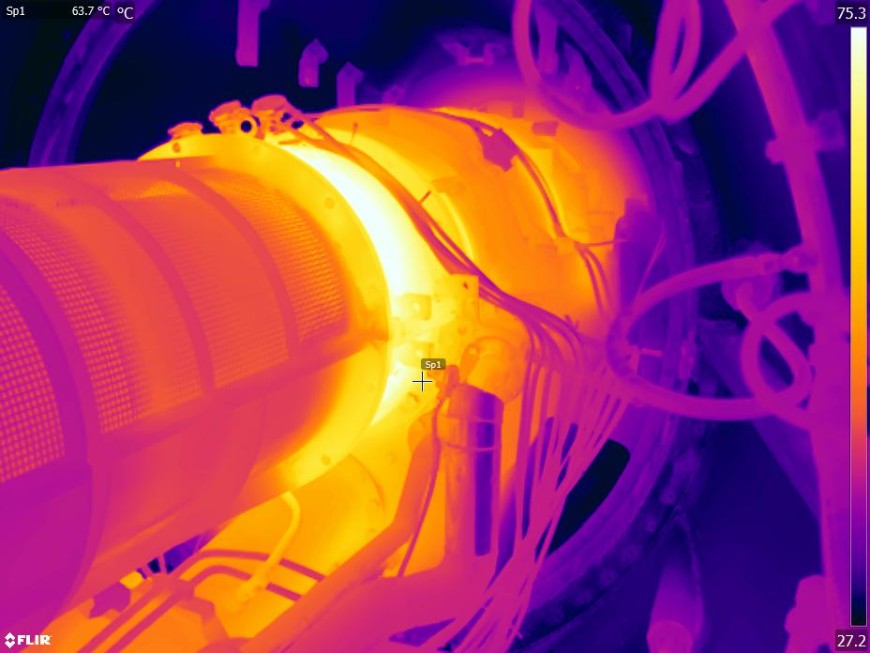
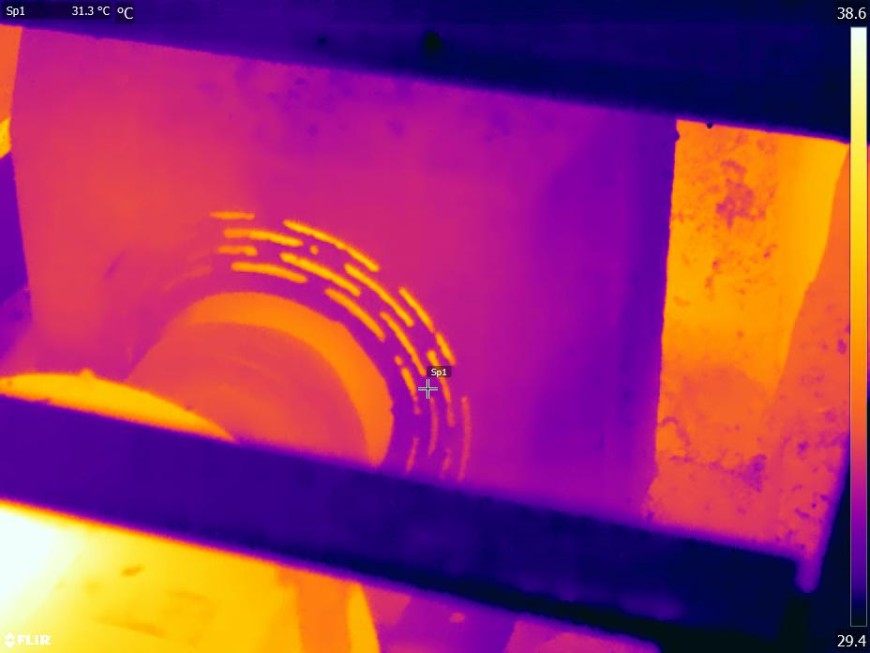
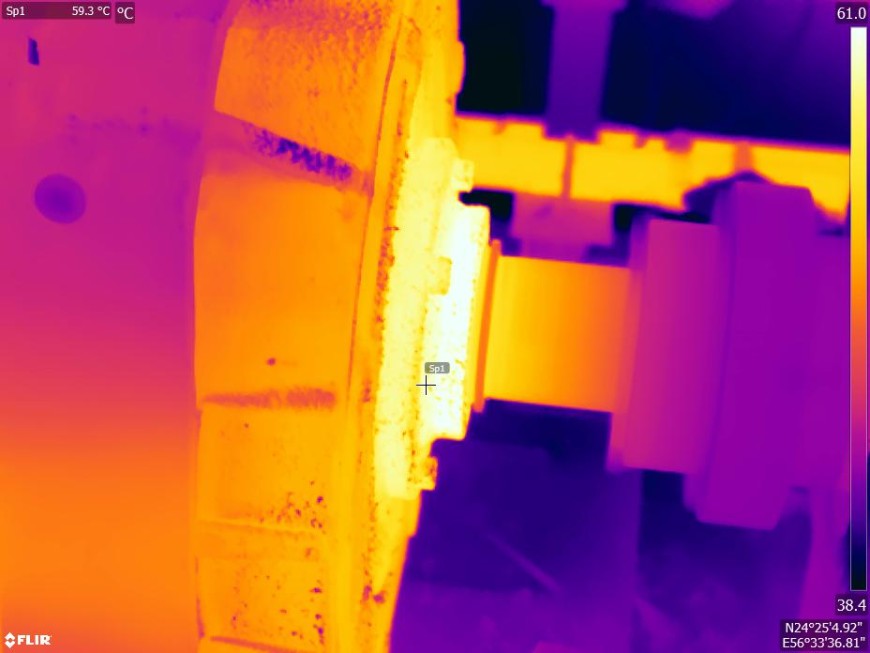
Thermal Imaging technology plays a vital role in inspection of mechanical rotary equipments along with vibration analysis and Airborne Ultrasound for Condition Monitoring. Along with troubleshooting, thermal imagers can also help optimize the production process itself as well as monitor quality control. Pumps, Motors, Turbines, Bearings, Conveyor belts, Process Valves and other mechanical machinery can be inspected and diagnosed with the help of thermal imaging. As a non-contact measurement tool that also makes invisible heat issues visible, thermal cameras let technicians inspect production equipment more safely even at peak operation.
Mechanical thermography inspections involve the use of thermal imaging technology to assess the performance, condition, and integrity of mechanical systems and equipment. Here are key points related to mechanical thermography inspections:
Purpose of Inspections:
Mechanical thermography inspections aim to identify potential issues or anomalies in mechanical systems and equipment. The inspections help detect abnormalities, such as overheating, faulty components, inadequate insulation, improper lubrication, or excessive friction. By identifying these issues, inspections contribute to improving reliability, energy efficiency, and preventing equipment failures.
Thermal Imaging Technology:
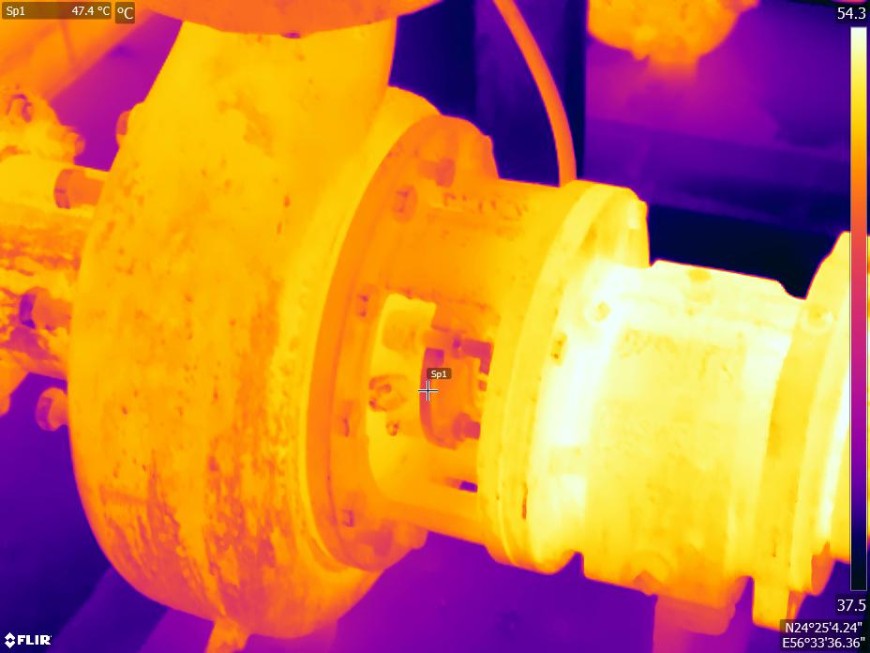
Thermal imaging cameras are used to capture infrared radiation emitted by the surfaces of mechanical equipment. These cameras detect temperature variations and generate visual images known as thermograms. Thermograms display different colors or temperature gradients, representing variations in temperature. By analyzing the thermograms, inspectors can identify areas of concern and evaluate the condition of the mechanical systems.
Equipment and Systems Inspected:
Mechanical thermography inspections can be performed on various types of equipment and systems, including motors, pumps, compressors, bearings, gearboxes, conveyors, heat exchangers, valves, and pipelines. The inspections are applicable to both rotating and stationary equipment in industrial, commercial, or residential settings.
Overheating Detection:
One of the primary objectives of mechanical thermography inspections is to detect overheating. Overheating can indicate issues such as bearing failure, misalignment, electrical problems, excessive friction, or inadequate cooling. Thermal imaging helps identify temperature anomalies that may not be visible to the naked eye, allowing for early intervention and maintenance.
Preventive Maintenance:
Mechanical thermography inspections contribute to preventive maintenance programs. By identifying potential problems before they escalate into major failures, inspections enable timely repairs or adjustments. This proactive approach reduces downtime, extends equipment lifespan, and minimizes repair costs.
Energy Efficiency:
Mechanical thermography inspections help identify energy efficiency opportunities by detecting energy losses or inefficiencies. For example, thermography can reveal insulation gaps or deficiencies, air leaks, or heat transfer issues. Addressing these issues can optimize energy consumption, reduce operational costs, and improve overall system performance.
Condition Monitoring:
Thermal inspections provide valuable insights into the condition of mechanical equipment over time. By conducting regular inspections and comparing thermograms, inspectors can track changes and trends in temperature patterns, identifying gradual degradation or developing faults. This information supports condition-based maintenance strategies.
Non-Destructive Testing:
Mechanical thermography inspections are non-destructive, meaning they do not require disassembly or physical contact with the equipment. This minimizes downtime and allows inspections to be performed while the equipment is in operation. Non-destructive testing is particularly advantageous for critical or hard-to-access components.
Reporting and Documentation:
Following a mechanical thermography inspection, a detailed report is typically prepared, documenting the findings, including identified issues, recommendations, and actions taken. This report serves as a reference for future inspections, aids in maintenance planning, and supports compliance documentation.
Professional Inspection Services:
Mechanical thermography inspections are often conducted by qualified thermographers or certified inspectors with expertise in mechanical systems and thermography. These professionals possess the knowledge and experience to accurately interpret thermal images, identify anomalies, and provide recommendations for maintenance or repairs.
Mechanical thermography inspections play a crucial role in ensuring the reliable performance, safety, and energy efficiency of mechanical systems and equipment. By detecting overheating, identifying potential issues, and supporting preventive maintenance, these inspections contribute to optimized operations, reduced downtime, and increased equipment lifespan.