Machinery Laser Shaft Alignment
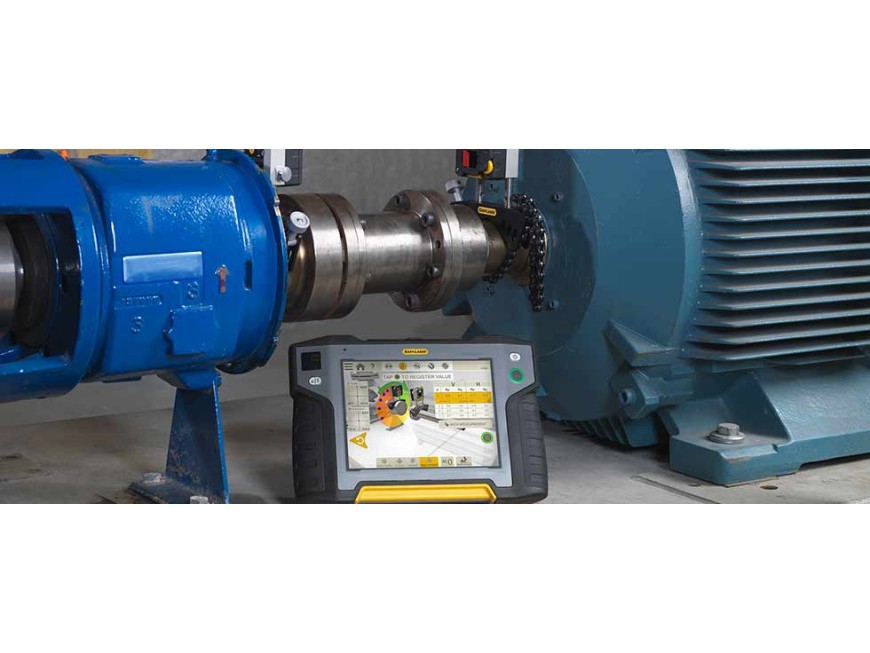
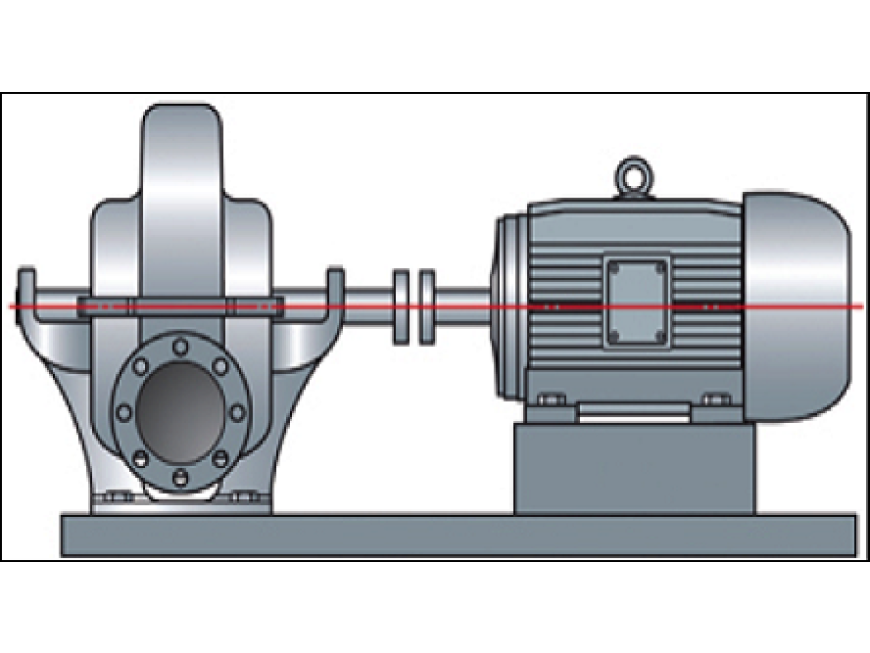
Laser shaft alignment (commonly known as coupling alignment) is the process of aligning two or more rotating shafts in a straight line. This involves looking at both the vertical and horizontal plane to try and ensure they are rotating on a common axis (coaxial)
Modern maintenance teams are up against complex alignment problems. So, beyond any one particular shaft alignment tool, teams need a laser alignment system that can cope with virtually any alignment problem. And with expertise shortages, these laser alignment systems need to work regardless of an operator’s experience and skill.
That’s where an adaptive laser shaft alignment system comes in. Thanks to modern software and other features, laser shaft alignment systems need to adapt to any situation and user experience level. A laser shaft alignment system also must maximize productivity as well as return on investment.
Traditional shaft alignment tools let users either diagnose or correct misalignment, but not both. A modern laser shaft alignment system identifies misalignment and can also calculate precise measurements to achieve alignment.
Single-laser Alignment System. A single-laser system eliminates the many frustrations and risks of inaccuracies that occur when working with two lasers firing in opposite directions. Single-laser alignment systems are faster than dual-laser ones, enable rapid completion of alignment tasks, and improve precision.
What are the uses of Laser Shaft Alignment Tools?
Laser shaft alignment tools have a wide range of applications in various industries where rotating machinery is present. Here are some common uses of these tools:
Rotating Machinery Alignment: The primary use of laser shaft alignment tools is to align rotating machinery such as pumps, motors, compressors, turbines, fans, and generators. These tools ensure that the shafts of the equipment are properly aligned to minimize misalignment-related issues.
Coupling Alignment: Laser shaft alignment tools are used to align couplings, which connect two shafts together. Proper alignment of couplings ensures smooth power transmission between the shafts and reduces wear on the coupling components.
Belt and Sheave Alignment: In systems that use belts and sheaves for power transmission, laser shaft alignment tools can be employed to align the pulleys and sheaves accurately. Proper alignment of these components improves belt life, reduces noise and vibration, and prevents premature failure.
Gearbox Alignment: Gearboxes are critical components in many machines, and misalignment can lead to increased wear, noise, and decreased efficiency. Laser shaft alignment tools help align the input and output shafts of gearboxes, ensuring optimal performance and reducing the risk of failure.
Shaft Alignment in Marine Applications: Laser alignment tools find extensive use in the marine industry to align propulsion systems, thrusters, and other rotating equipment on ships and offshore installations. Proper alignment in marine applications is crucial for efficient operation and avoiding unnecessary vibrations.
Alignment in Power Plants: Power plants, including thermal power plants, hydroelectric plants, and wind farms, rely on numerous rotating machinery components. Laser shaft alignment tools help align turbines, generators, pumps, and other equipment to maintain their efficiency and reliability.
Alignment in Manufacturing Processes: Laser shaft alignment tools are used in manufacturing facilities to align machinery used in production lines, such as conveyors, rollers, and presses. Accurate alignment ensures consistent output, reduces downtime, and improves product quality.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting: Laser alignment tools are valuable for maintenance and troubleshooting activities. They help identify misalignment issues and assist technicians in making the necessary adjustments or repairs to restore proper alignment.
These are just a few examples of the diverse applications of laser shaft alignment tools. Their versatility and accuracy make them indispensable in industries where precise alignment of rotating machinery is essential for optimal performance, reliability, and safety.