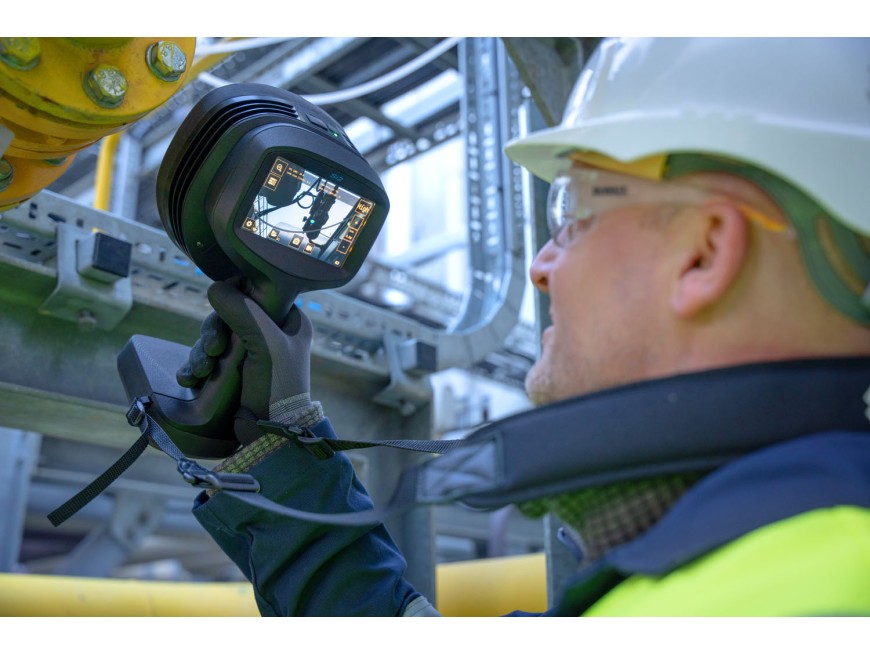
Acoustic imaging for mechanical fault detection is an innovative technique that utilizes sound-based technology to detect, localize, and analyze faults in mechanical systems. This approach is particularly valuable for preventive maintenance and condition monitoring, as it allows for early detection of anomalies before they evolve into serious failures. Let’s delve into how acoustic imaging works, its applications, and the advantages it offers in mechanical fault detection.
How Acoustic Imaging Works
-
Sound Wave Capture: Acoustic imaging involves capturing sound waves emitted by machinery during operation. These sounds may include normal operating noises as well as any abnormal sounds indicative of mechanical issues such as friction, impacts, or vibrations.
-
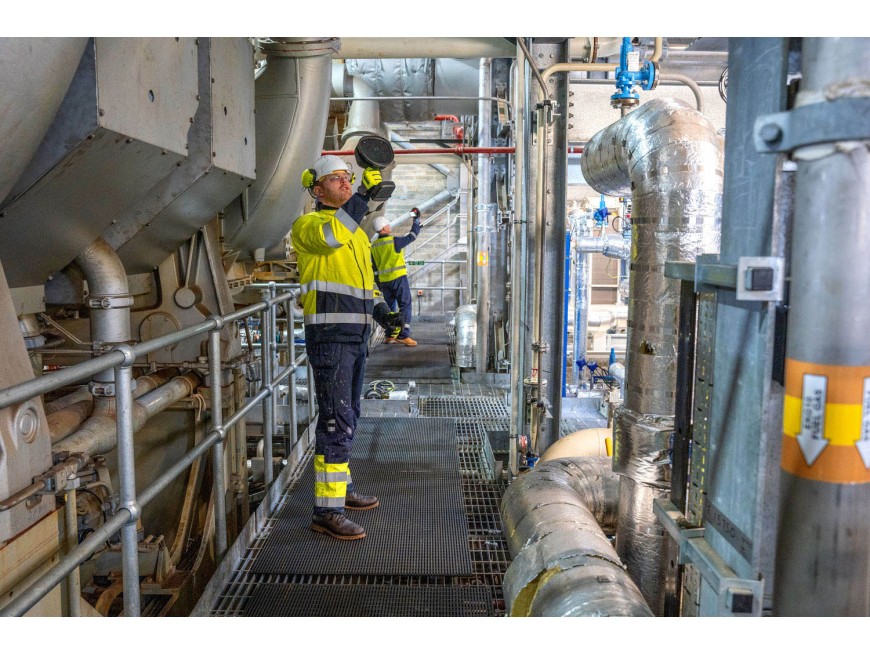
Sensor Array: An array of microphones or acoustic sensors is typically used to capture noise at various points around the equipment. Advanced systems might also integrate laser vibrometry to assess vibration patterns.
-
Data Analysis: The collected sound data is then analyzed using signal processing techniques. This can involve Fourier transforms, wavelet transforms, or other methods to transform sound waves into a format that can be easily analyzed for abnormalities.
-
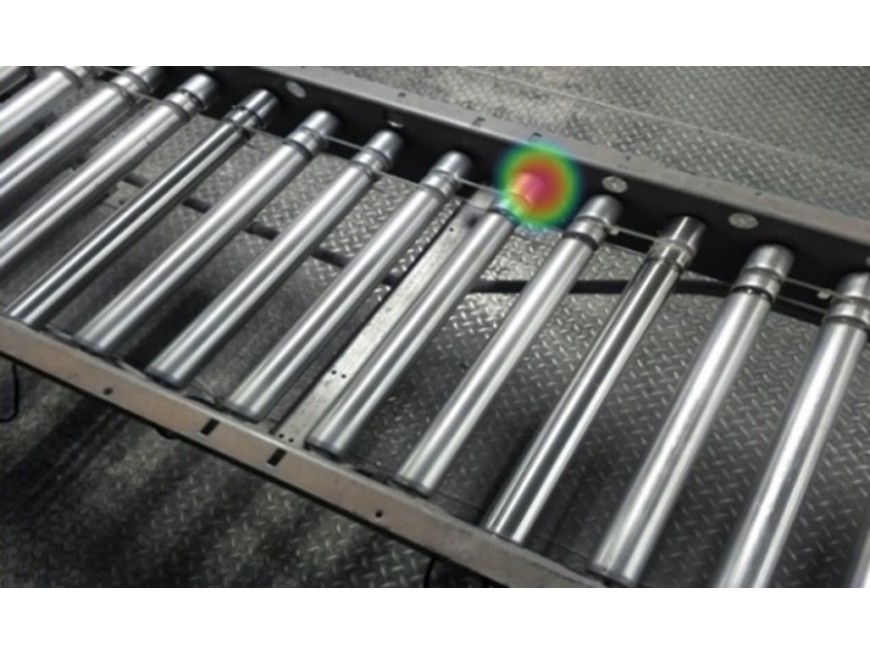
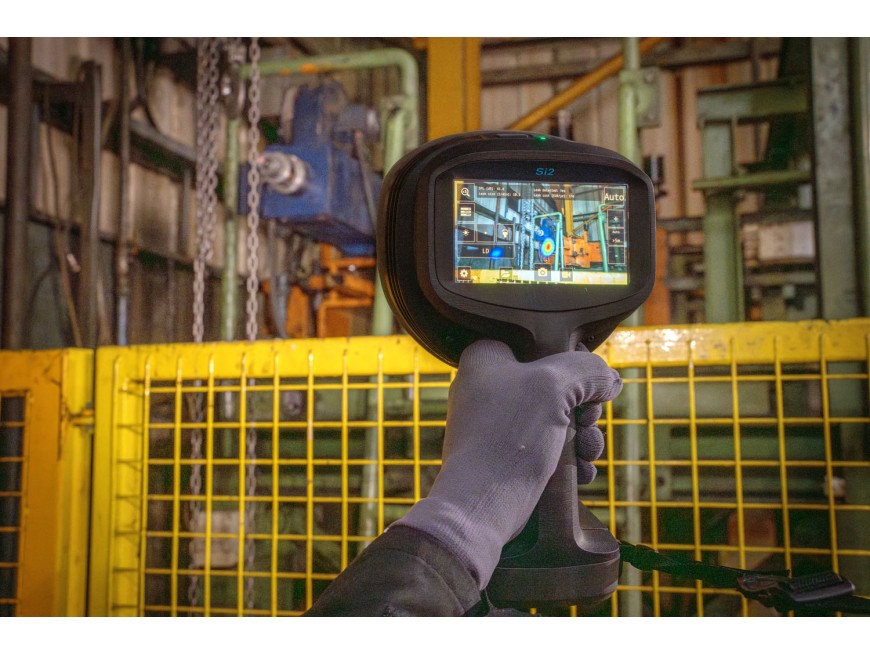
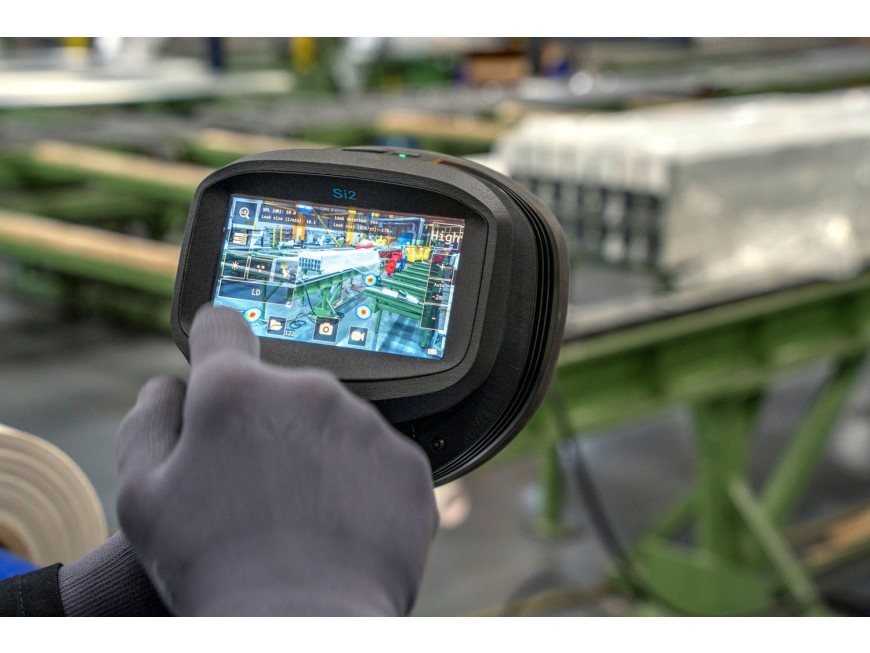
Imaging and Visualization: The processed data is converted into an image or a set of images that represent the sound emissions from the machine. These images help in visualizing the distribution of sound intensities and identifying areas where unusual noise levels indicate potential issues.
-
Diagnostics: Using algorithms and machine learning models, the system can diagnose specific types of faults such as bearing failures, misalignment, imbalance, or lubrication issues based on the acoustic signatures captured.
Applications
- Industrial Machinery: Monitoring rotating machinery such as bearings, rollers, conveyors, pulleys, turbines, compressors, and motors.
- Automotive: Detecting faults in engines and transmission systems.
- Aerospace: Inspection of aircraft engines and components for cracks or other structural failures that affect sound emissions.
- HVAC Systems: Identifying issues in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, including leak detection.
Advantages of Acoustic Imaging
- Non-Invasive: Acoustic imaging is a non-contact method, which means it does not require the disassembly of machinery or any direct interaction with the operational parts.
- Early Detection: It can detect the precursors to mechanical failures at a very early stage, enabling preventive maintenance before costly breakdowns occur.
- Cost-Effective: Reduces the need for frequent physical inspections and minimizes downtime by allowing for more precise scheduling of maintenance activities.
- Safety: Enhances safety by detecting faults that could lead to hazardous conditions if left unchecked.
- Comprehensive Monitoring: Allows for the monitoring of equipment even in inaccessible areas or in harsh environments.