


Machinery Laser Shaft Alignment
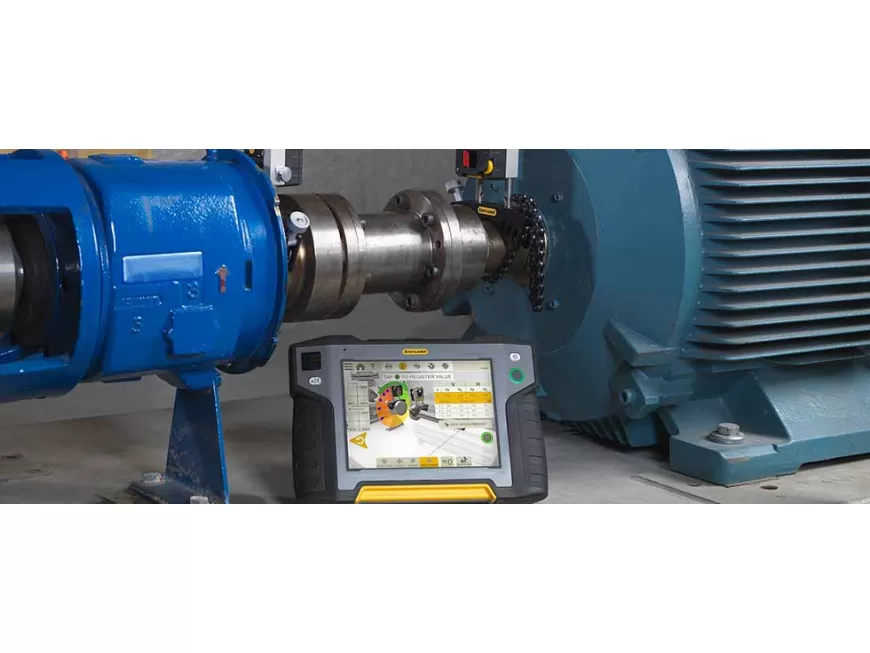
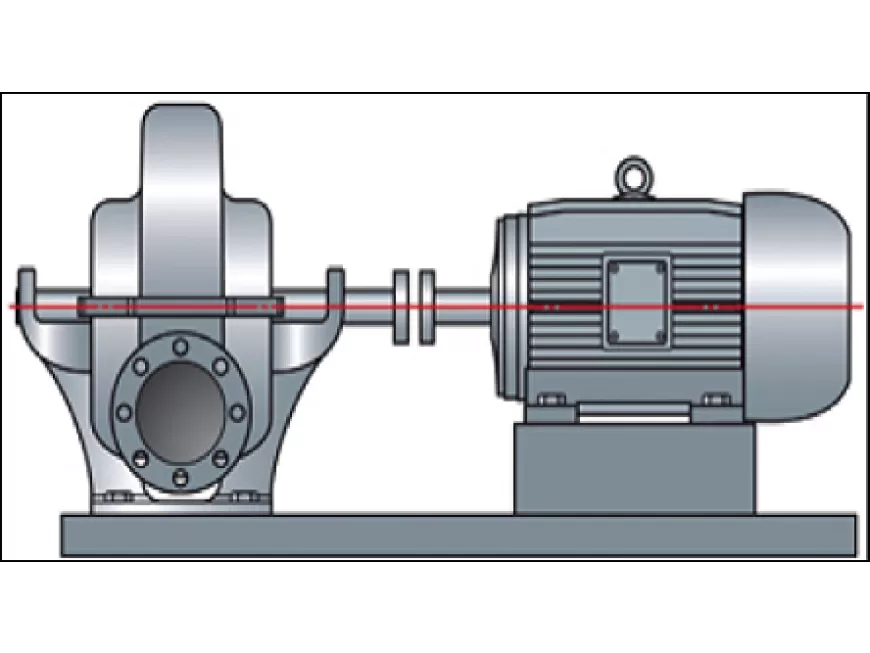
Laser shaft alignment (commonly known as coupling alignment) is the process of aligning two or more rotating shafts in a straight line. This involves looking at both the vertical and horizontal plane to try and ensure they are rotating on a common axis (coaxial)
Modern maintenance teams are up against complex alignment problems. So, beyond any one particular shaft alignment tool, teams need a laser alignment system that can cope with virtually any alignment problem. And with expertise shortages, these laser alignment systems need to work regardless of an operator’s experience and skill.
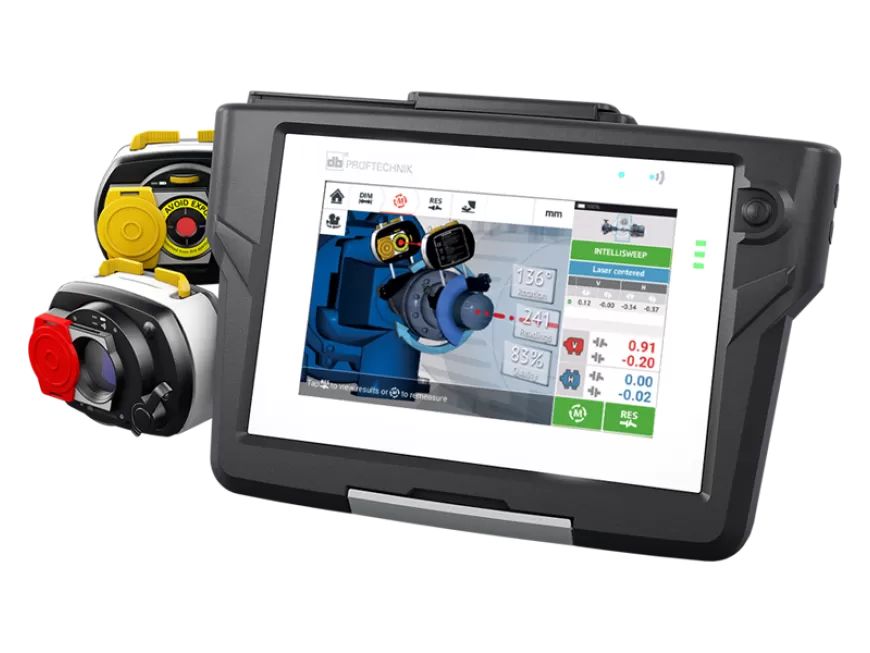
That’s where an adaptive laser shaft alignment system comes in. Thanks to modern software and other features, laser shaft alignment systems need to adapt to any situation and user experience level. A laser shaft alignment system also must maximize productivity as well as return on investment.
Traditional shaft alignment tools let users either diagnose or correct misalignment, but not both. A modern laser shaft alignment system identifies misalignment and can also calculate precise measurements to achieve alignment.
Single-laser Alignment System. A single-laser system eliminates the many frustrations and risks of inaccuracies that occur when working with two lasers firing in opposite directions. Single-laser alignment systems are faster than dual-laser ones, enable rapid completion of alignment tasks, and improve precision.
What are the uses of Laser Shaft Alignment Tools?
Laser shaft alignment tools have a wide range of applications in various industries where rotating machinery is present. Here are some common uses of these tools:
Rotating Machinery Alignment
Coupling Alignment
Belt and Sheave Alignment
Gearbox Alignment
Shaft Alignment in Marine Applications
Alignment in Power Plants
Alignment in Manufacturing Processes
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
These are just a few examples of the diverse applications of laser shaft alignment tools. Their versatility and accuracy make them indispensable in industries where precise alignment of rotating machinery is essential for optimal performance, reliability, and safety.



